Helping Trees Stand the Test of Time
At Arbor Aesthetics, we are a full-service tree care company with a deep appreciation for trees and the role they play in our lives. Every day, we see how trees provide shade, shelter, food, and materials that humans have relied on for generations. At the same time, trees face constant environmental pressures. However, one internal structure gives trees the strength to endure harsh environments and stand for decades: heartwood.
As the dense, supportive core of a tree, heartwood plays a critical role in long-term stability, durability, and resistance to decay.

Basic Tree Anatomy
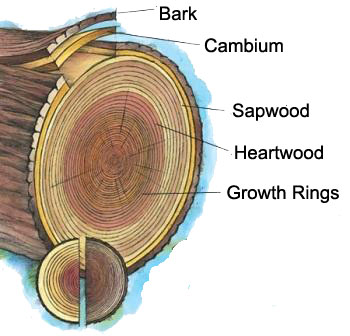
To fully understand heartwood, it helps to first review basic tree anatomy. Trees consist of six primary layers: outer bark, inner bark, cambium, sapwood, heartwood, and pith[i]
Each spring, the cambium produces phloem and xylem[ii] Phloem carries sugars and nutrients from the leaves downward. Xylem transports water and minerals upward from the roots. Over time, as trees age, older xylem transitions into sapwood[iii] and eventually becomes heartwood.
[i] https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/heartwood
[ii] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168945219314955
[iii] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1631069110000119
From Sapwood to Heartwood
As sapwood ages, it thickens and undergoes lignification. This process strengthens cell walls and reduces permeability. At the same time, the tree initiates programmed cell death within these cells. As a result, the tree forms heartwood.[i]
Because of this process, heartwood develops only in mature trees and often takes more than ten years to form. Unlike sapwood, heartwood does not transport water. Instead, it provides structural strength and resists decay, rot, and environmental stress[ii]. Meanwhile, chemical changes within the wood cells give heartwood its darker color[iii].
[i] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1631069110000119#fig1
[ii] https://www.fs.usda.gov/learn/trees/anatomy-of-tree
[iii] https://extension.psu.edu/what-is-heartwood-in-trees
Why Heartwood Matters
Because this inner core provides rigidity, it allows trees to grow tall, withstand storms, and survive for long periods. Although it no longer participates in active growth, it continues to support the living outer layers. Consequently, the tree can keep producing new growth rings year after year.
Even after a tree’s life ends, this durable wood still serves a purpose. For this reason, its strength makes it ideal for lumber used in homes, furniture, and infrastructure. In turn, this use extends the tree’s legacy far beyond its lifespan.

Caring for Trees That Last
At Arbor Aesthetics, we focus on long-term tree health so trees can build internal strength naturally. To achieve this goal, proper pruning, soil management, and plant health care all play important roles. In addition, professional oversight helps trees maintain the conditions needed to develop dense, resilient wood over time.
Ultimately, our promise is simple: Beautiful Trees for Life. Therefore, from pruning and trimming to plant health care, our Certified Arborists help trees grow strong from the inside out. Contact Arbor Aesthetics today to schedule a consultation and invest in the long-term strength of your trees.
Heartwood
“Euphoric is the reward of my reach
Tasting the light, oh so sweet
Touching the face of what man cannot see,
Is the joy of my days, short though they be
Under my boughs the children played
Shelter for them, I proved to be
I now cast my seeds in the streams of the wind
To carry on long after me
Let no one be sad at the sound of my fall
I’m just laying down in times bed
Though I still stood erect many years without leaves
The fact of the matter, I have long been dead
Yet, euphoric was the reward of my reach”
by Bill Cantrell, 2019 [vi]
[i] https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/heartwood
[ii] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168945219314955
[iii] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1631069110000119
[iv] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1631069110000119#fig1
[v] https://www.fs.usda.gov/learn/trees/anatomy-of-tree
[vi] https://extension.psu.edu/what-is-heartwood-in-trees






